Introduction:
Adaptive reuse is when a property is repurposed for a different use while retaining any historic structures or features of the original building.
Adaptive reuse can be a very useful option for owners or developers interested in maximizing a historic property’s value.
Key Takeaways:
- Adaptive reuse involves repurposing a property for a different use while preserving its historic structures and features.
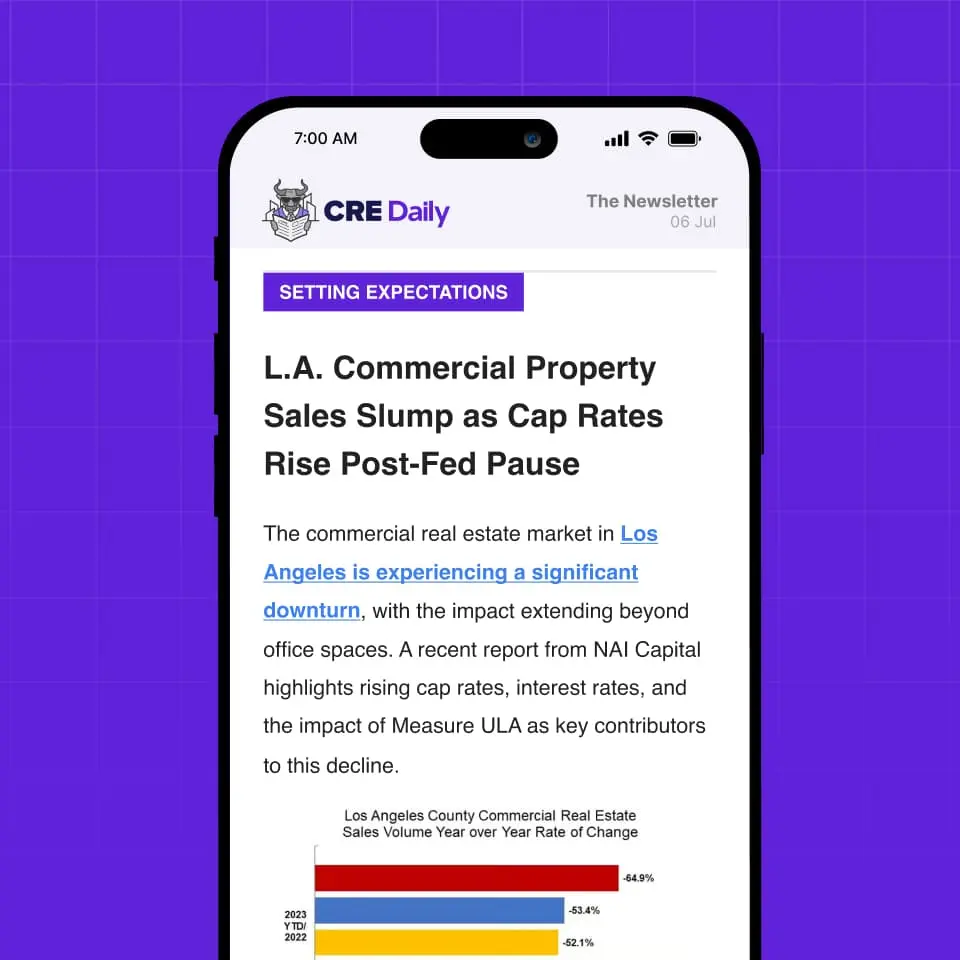
- Converting properties is gaining popularity in various asset classes, including converting office buildings into multifamily housing, retail buildings into co-living spaces, and old factories into modern workspaces.
How it Works:
Adaptive reuse involves identifying a property with the potential for repurposing and transforming it into a different use while preserving its historic features.
Investors should evaluate the property’s location, conduct due diligence on design, engineering, land use, construction, and finances.
They should also navigate zoning regulations, code compliance, and any potential challenges that may arise during the design and construction process.
Key Components:
- Prime Location: The success of an adaptive reuse project heavily depends on selecting a property in a high-traffic area with similar uses to the desired repurposing.
- Zoning Regulations and Code Compliance: Investors must research and navigate zoning regulations and code compliance, which may require months of paperwork and adjustments to meet modern standards and fire safety requirements.
- Challenges: Challenges in adaptive reuse projects include bringing the building up to code, addressing hazardous materials, investing additional money for updates, and dealing with complex federal historic tax incentives.
Benefits:
- Economic Sustainability: Adaptive reuse minimizes waste, materials, and emissions by utilizing pre-existing structures, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
- Community Impact: Converting commercial properties into residential or mixed-use spaces reduces traffic and parking requirements while fostering walkable communities and preserving cultural history.
- Potential Cost Savings: While adaptive reuse projects may require initial investments to bring the property up to modern standards, repurposing existing structures can save on construction costs compared to developing from scratch.
Takeaway:
As the commercial real estate industry continues to prioritize economically sustainable and resourceful construction methods, adaptive reuse projects offer opportunities to repurpose existing structures for new purposes.
With considerations for location, zoning regulations, code compliance, and potential challenges, adaptive reuse allows investors to unlock a property’s maximum value while preserving architectural history and minimizing environmental impact.
However, it is important to note that adaptive reuse projects come with complexities, such as navigating zoning and code compliance, addressing hazardous materials, and considering federal historic tax incentives.
Therefore, investors should work with experienced professionals and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure the success of their adaptive reuse endeavors.
Disclaimer: The information on this website, including glossary definitions, is for educational and informational purposes only and not intended as professional advice. While we strive for accuracy, we make no guarantees regarding the completeness, reliability, or timeliness of the information provided. We are not liable for any loss or damage arising from your use of the site. Investment decisions in commercial real estate should be made based on individual due diligence and professional advice. Laws and regulations are subject to change; always consult legal and financial experts before making decisions.
Sources:
https://www.crexi.com/insights/what-to-know-about-adaptive-reuse-in-commercial-real-estate