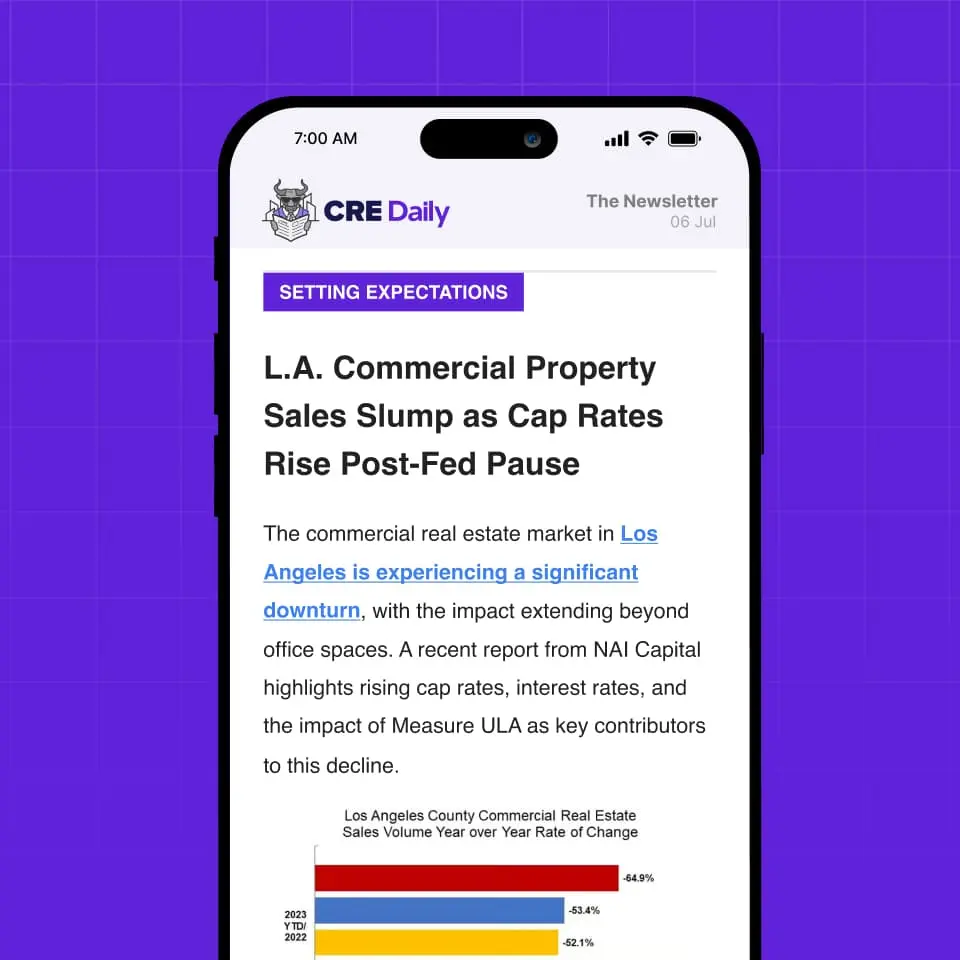
- The CMBS special servicing rate rose 45 bps in February 2025, reaching 10.32%.
- Retail and office property loans were the primary contributors to the surge.
- Office loans accounted for 78% of new transfers to special servicing, a notable increase.
The cmbs special servicing rate spiked up in February, rising 45 bps to 10.32%. This came after a brief dip in January, which was the first drop in over a year, per Trepp.
Napkin Math
The rate surge was largely due to two factors: a $1.8B rise in the net balance of loans in special servicing and a $8.8B drop in the overall balance of loans outstanding.
As a result, the rate jumped because a larger numerator (the loans in special servicing) was divided by a smaller denominator (the total balance of loans).
Retail, Office in Lead
Two property types—retail and office—were the primary drivers behind the surge in the special servicing rate:
- The retail loan rate increased by 59 bps to 11.26%, reversing a 100-bp drop in January.
- The office loan rate soared by 108 bps to 16.19%, reaching its highest level in over 25 years.
Mixed-Use Properties
Mixed-use properties also saw a big rise, with the special servicing rate climbing 33 bps to 13.04%. This marks the first time in over a decade that the mixed-use rate surpassed the 13% threshold.
Get Smarter about what matters in CRE
Stay ahead of trends in commercial real estate with CRE Daily – the free newsletter delivering everything you need to start your day in just 5-minutes
Office Dominates Transfers
In February, new transfers to special servicing totaled just over $2.3B. Office loans accounted for the majority of the increase, with $1.8B in office loans contributing nearly 78% of the monthly total.
This was a steep jump from January, where office loans transferred to special servicing were half that volume.
Looking Ahead
The sharp rise in the CMBS special servicing rate reveals ongoing challenges in the office and retail sectors. The rise in special servicing suggests more challenges ahead for these sectors, with potential long-term implications for CMBS performance.